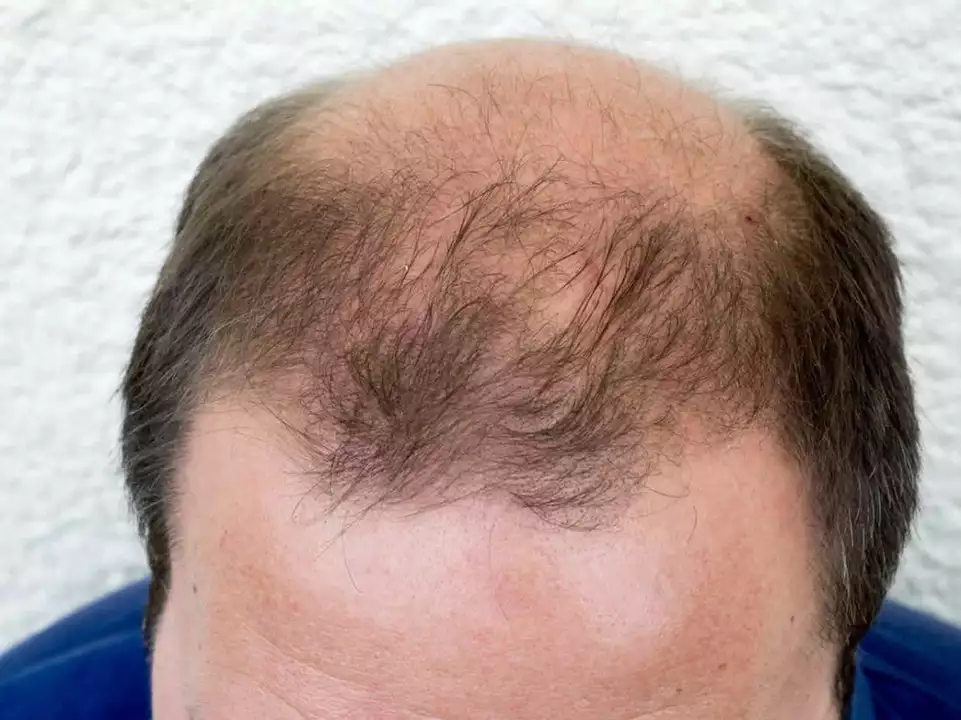
Androgenic Alopecia: What You Need to Know
If you've noticed your hair thinning or receding, androgenic alopecia might be the cause. It’s the scientific term for what’s commonly called male or female pattern baldness. This is the most common type of hair loss affecting millions worldwide, often linked to genetics and hormones. But understanding it helps you take control instead of feeling stuck.
Androgenic alopecia happens when hair follicles shrink due to a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This hormone basically tells your hair roots to stop growing thick hair and instead produce finer, shorter hairs until they eventually stop growing altogether. This process often starts with a receding hairline in men or thinning on the crown and progresses over time.
Who Gets Affected and Why?
Both men and women can have androgenic alopecia, but it usually looks different in each. Men often see a classic pattern: a receding hairline and bald spots on the crown. Women tend to have a general thinning on the top of the head but rarely go completely bald. Genetics play a strong role here — if close relatives have experienced this kind of hair loss, your chances increase. Age is another big factor; it tends to start in your 20s or 30s and progresses gradually.
How Can You Manage or Treat It?
Good news—there are options to slow down hair loss and even regrow some hair. Over-the-counter treatments like minoxidil can help keep hair follicles alive longer and encourage growth. Prescription medications such as finasteride work by lowering DHT levels but require a doctor's advice due to possible side effects. For some, hair transplants are another solution, moving healthy follicles to thinning areas. And don’t underestimate lifestyle choices: eating a balanced diet, reducing stress, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can support healthier hair growth.
Got questions about your hair loss? Remember, acting early often gives you more options. Talking with a healthcare provider can help clarify what’s right for your situation. And whatever path you choose, having solid information handy will help you make confident decisions about your hair and health.
Androgenic Alopecia and Hair Loss in the LGBTQ+ Community
As a blogger, I recently explored the topic of Androgenic Alopecia and hair loss in the LGBTQ+ community. I discovered that this form of hair loss impacts people of all genders and sexual orientations, but may be particularly distressing for transgender and gender non-conforming individuals. Hormone therapy can sometimes exacerbate or trigger this condition, which can be especially challenging for those undergoing gender-affirming treatments. It's important for the LGBTQ+ community to have access to support and resources tailored to their unique experiences with hair loss. By raising awareness and encouraging open dialogue, we can work together to improve the mental well-being and self-esteem of those affected.